DataSets y DataLoaders
Contents
DataSets y DataLoaders#
Introducción#
El código para procesar muestras de datos puede resultar complicado y difícil de mantener; idealmente queremos que nuestro código de datasets se desacople de nuestro código de entrenamiento modelo para una mejor legibilidad y modularidad. PyTorch proporciona dos primitivas de datos: torch.utils.data.DataLoader y torch.utils.data.Dataset que le permiten utilizar conjuntos de datos precargados, así como sus propios datos.
Dataset almacena las muestras y sus etiquetas correspondientes, y DataLoader envuelve un iterable alrededor del conjunto de datos para permitir un fácil acceso a las muestras.
Carga de un Dataset#
import torch
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torchvision import datasets
from torchvision.transforms import ToTensor
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
training_data = datasets.FashionMNIST(
root="data",
train=True,
download=True,
transform=ToTensor()
)
test_data = datasets.FashionMNIST(
root="data",
train=False,
download=True,
transform=ToTensor()
)
Iterando y visualizando el dataset#
label_map = {
0: 'Tshirt',
1: "Trouser",
2: "Pullover",
3: "Dress",
4: "Coat",
5: "Sandal",
6: "Shirt",
7: "Sneaker",
8: "Bag",
9: "Ankle Boot",
}
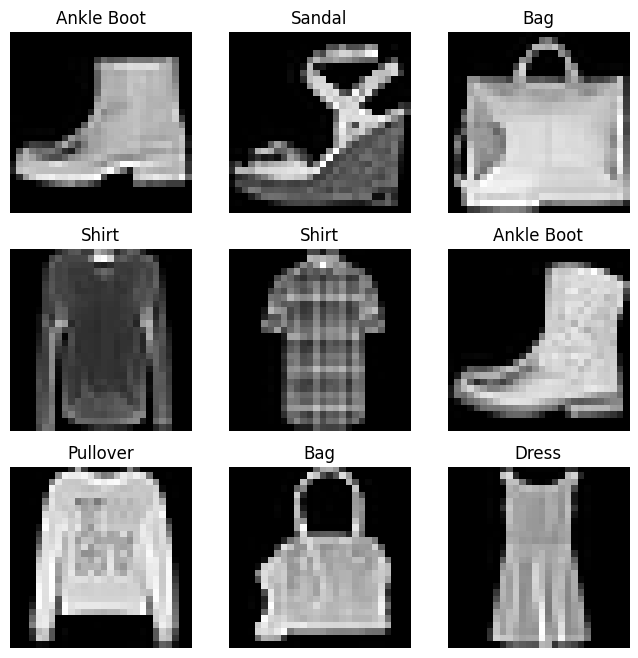
figure = plt.figure(figsize=(8,8))
cols, rows = 3,3
for i in range(1, cols*rows+1):
sample_idx = torch.randint(len(training_data), size =(1,)).item()
img, label = training_data[sample_idx]
figure.add_subplot(rows, cols, i)
plt.title(label_map[label])
plt.axis('off')
plt.imshow(img.squeeze(), cmap='gray')
plt.show()

img.shape
torch.Size([1, 28, 28])
Creación de un conjunto de datos personalizado para sus archivos#
En este ejemplo, las imágenes FashionMNIST se almacenan en un directorio img_dir, y sus etiquetas se almacenan por separado en un archivo CSV annotations_file.
import os
import pandas as pd
from torchvision.io import read_image
class CustomImageDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, annotation_file, img_dir, transform=None, target_transform=None):
self.img_labels = pd.read_csv(annotation_file)
self.img_dir = img_dir
self.transform = transform
self.target_transform = target_transform
def __len__(self):
return len(self.img_labels)
def __get_item__(self, idx):
img_path = os.path.join(self.img_dir, self.img_labels.iloc[idx, 0])
image = read_image(img_path)
label = self.image_labels.iloc[idx, 1]
if self.transform:
image = self.transform(image)
if self.target_transform:
label = self.target_transform(label)
return image, label
Las etiquetas (labels) del archivo en el ejemplo labels.csv lucen como
Leemos los datos desde una archivo comprimido#
Los datos fueron bajados desde la fuente usando wget. Por favor revise los detalles. Para Windows revise aquí
!wget http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz
!wget http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz
!wget http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz
!wget http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz
--2022-08-30 21:42:38-- http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz
Resolving yann.lecun.com (yann.lecun.com)... 172.67.171.76, 104.21.29.36, 2606:4700:3034::6815:1d24, ...
Connecting to yann.lecun.com (yann.lecun.com)|172.67.171.76|:80... connected.
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
Length: 9912422 (9.5M) [application/x-gzip]
Saving to: ‘train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz’
train-ima 0%[ ] 0 --.-KB/s
train-images-idx3-u 100%[===================>] 9.45M --.-KB/s in 0.06s
2022-08-30 21:42:38 (147 MB/s) - ‘train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz’ saved [9912422/9912422]
--2022-08-30 21:42:38-- http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz
Resolving yann.lecun.com (yann.lecun.com)... 104.21.29.36, 172.67.171.76, 2606:4700:3036::ac43:ab4c, ...
Connecting to yann.lecun.com (yann.lecun.com)|104.21.29.36|:80... connected.
HTTP request sent, awaiting response...
200 OK
Length: 28881 (28K) [application/x-gzip]
Saving to: ‘train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz’
train-lab 0%[ ] 0 --.-KB/s
train-labels-idx1-u 100%[===================>] 28.20K --.-KB/s in 0s
2022-08-30 21:42:38 (317 MB/s) - ‘train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz’ saved [28881/28881]
--2022-08-30 21:42:38-- http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz
Resolving yann.lecun.com (yann.lecun.com)... 104.21.29.36, 172.67.171.76, 2606:4700:3036::ac43:ab4c, ...
Connecting to yann.lecun.com (yann.lecun.com)|104.21.29.36|:80... connected.
HTTP request sent, awaiting response...
200 OK
Length: 1648877 (1.6M) [application/x-gzip]
Saving to: ‘t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz’
t10k-imag 0%[ ] 0 --.-KB/s
t10k-images-idx3-ub 100%[===================>] 1.57M --.-KB/s in 0.07s
2022-08-30 21:42:38 (22.3 MB/s) - ‘t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz’ saved [1648877/1648877]
--2022-08-30 21:42:38-- http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz
Resolving yann.lecun.com (yann.lecun.com)... 104.21.29.36, 172.67.171.76, 2606:4700:3036::ac43:ab4c, ...
Connecting to yann.lecun.com (yann.lecun.com)|104.21.29.36|:80... connected.
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
Length: 4542 (4.4K) [application/x-gzip]
Saving to: ‘t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz’
t10k-labe 0%[ ] 0 --.-KB/s
t10k-labels-idx1-ub 100%[===================>] 4.44K --.-KB/s in 0s
2022-08-30 21:42:38 (142 MB/s) - ‘t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz’ saved [4542/4542]
Imágenes de entrenamiento#
import gzip
f = gzip.open('./data/FashionMNIST/raw/train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz','r')
image_size = 28
num_images = 60000
import numpy as np
f.read(16) # omite los primeros 16 bytes
buf = f.read(image_size * image_size * num_images)
data_train = np.frombuffer(buf, dtype=np.uint8).astype(np.float32)
data_train = data_train.reshape(num_images, image_size, image_size, 1)
print(data_train.shape)
(60000, 28, 28, 1)
Etiquetas de entrenamiento#
import gzip
f = gzip.open('./data/FashionMNIST/raw/train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz','r')
num_labels = 60000
import numpy as np
f.read(8) # omite los primeros 8 bytes
buf = f.read(num_labels)
label_train = np.frombuffer(buf, dtype=np.uint8).astype(np.int64)
print(label_train.shape)
print(label_train[:20])
(60000,)
[9 0 0 3 0 2 7 2 5 5 0 9 5 5 7 9 1 0 6 4]
Imágenes de test#
import gzip
f = gzip.open('./data/FashionMNIST/raw/t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz','r')
image_size = 28
num_images = 10000
import numpy as np
f.read(16) # omite los primeros 16 bytes
buf = f.read(image_size * image_size * num_images)
data_test = np.frombuffer(buf, dtype=np.uint8).astype(np.float32)
data_test = data_test.reshape(num_images, image_size, image_size, 1)
print(data_test.shape)
(10000, 28, 28, 1)
Etiquetas de test#
import gzip
f = gzip.open('./data/FashionMNIST/raw/t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz','r')
num_labels = 10000
import numpy as np
f.read(8) # omite los primeros 8 bytes
buf = f.read(num_labels)
label_test = np.frombuffer(buf, dtype=np.uint8).astype(np.int64)
print(label_test.shape)
print(label_test[:20])
(10000,)
[9 2 1 1 6 1 4 6 5 7 4 5 7 3 4 1 2 4 8 0]
Crea datasets para estos datos#
class ImageDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, labels, images, transform=None, target_transform=None):
self.labels = labels
self.images = images
self.transform = transform
self.target_transform = target_transform
def __len__(self):
return len(self.labels)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
image = self.images[idx]
label = self.labels[idx]
if self.transform:
image = self.transform(image)
if self.target_transform:
label = self.target_transform(label)
return image, label
train_dataset = ImageDataset(label_train, data_train)
test_dataset = ImageDataset(label_test, data_test)
Preparando sus datos para entrenamiento con DataLoaders#
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
train_dataloader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=64, shuffle=True)
test_dataloader = DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=64, shuffle=True)
test_dataloader
<torch.utils.data.dataloader.DataLoader at 0x7f044039c190>
Iterando a lo largo del DataLoader#
Cada iteración retorna un batch (batch_size=64) de datos (train_features y train_labels). Dado que shuffel=True en el ejemplo, todos los lotes de datos se mezclan. Un control mpas fino para establecer el orden se obtiene usando Samplers.
# Despliega imagen y etiqueta
train_features, train_labels = next(iter(train_dataloader))
print(f'Feature batch shape: {train_features.size()}')
print(f'Labels batch shape: {train_labels.size()}')
img = train_features[0].squeeze()# primer elemento del batch
# squeeze elimina ejes de tamaño 1.
label = train_labels[0]
plt.imshow(img, cmap='gray')
plt.show()
print(f'Label: {label}')
Feature batch shape: torch.Size([64, 28, 28, 1])
Labels batch shape: torch.Size([64])
Label: 6


